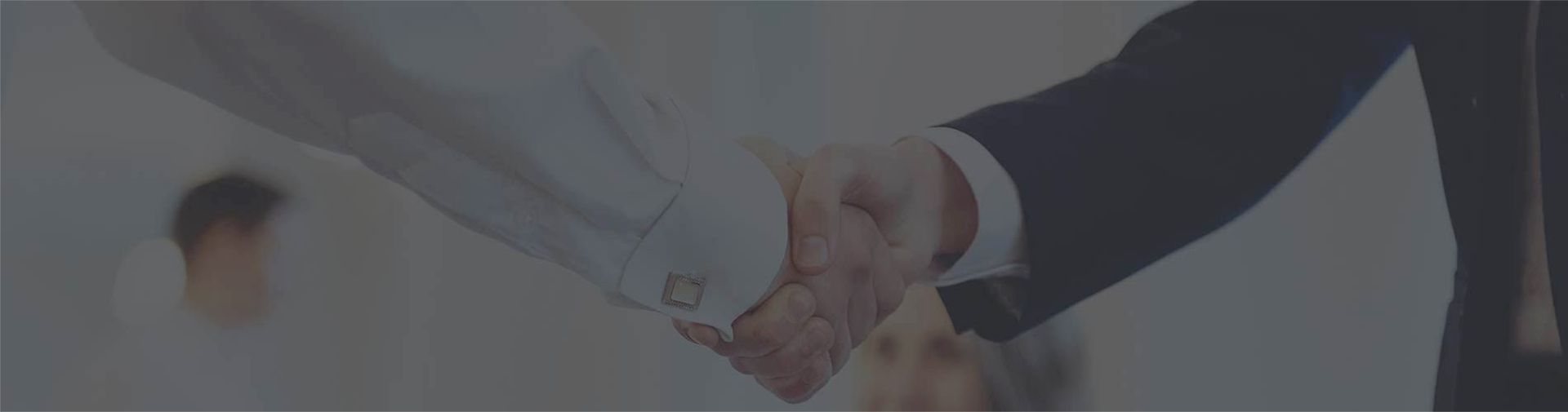
Sheet metal often incurs warping, residual stresses, or uneven surfaces during processes like laser cutting, stamping, or transportation. These defects lead to:
Assembly challenges: Misaligned parts increase rework time.
Reduced durability: Internal stresses weaken structural integrity.
Aesthetic flaws: Uneven surfaces affect coatings or finishes.
Advanced leveling methods eliminate these issues, ensuring materials meet strict tolerances and perform reliably in end-use applications.
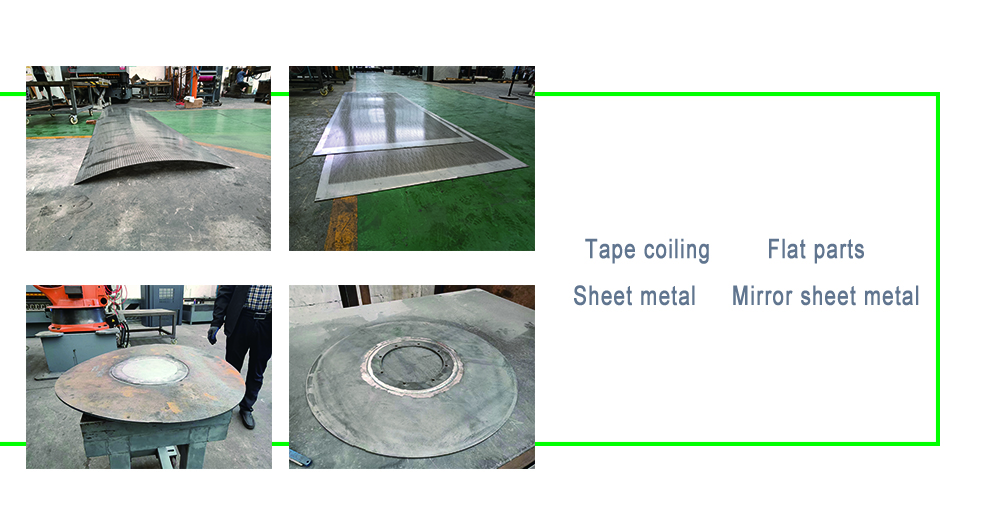
Cutting-Edge Sheet Metal Leveling Methods Compared
1. Straightening Press: Precision for Heavy-Duty Applications
Ideal for thick plates (>50 mm), this method uses hydraulic force to target localized deformities.
Process:
Advantages:
Limitations:
Best For: Repairing thick plates or custom fabrication projects.
2. Rolling Machines: Affordable but Limited Precision
A cost-effective option for thin sheets, rolling machines use three offset rollers to bend metal into shape.
Process:
Advantages:
Limitations:
Fails to address internal stresses.
Time-consuming for complex defects.
Safety risks in manual setups.
Best For: Workshops processing thin sheets with basic flatness needs.
3. Simple Roller Levelers: Balancing Speed and Quality
Equipped with 7+ large rollers, these systems handle moderate thicknesses but lack precision.
Process:
Advantages:
Limitations:
Best For: General-purpose workshops with mixed production demands.
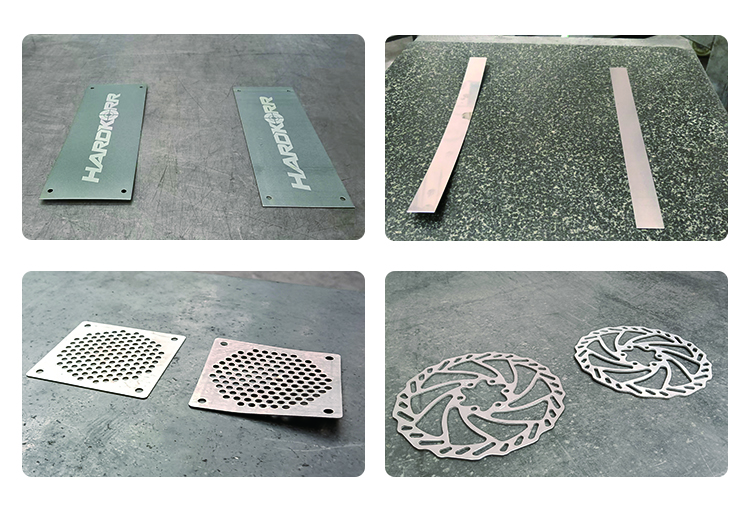
4. Precision Levelers: The Future of High-Volume Fabrication
Modern precision levelers use tightly packed, supported rollers to eliminate stresses and deliver ultra-flat sheets.
Process:
Advantages:
Produces stress-free, laser-cut-ready sheets.
Reduces scrap rates by 20-30%.
Automated for high-speed production.
Limitations:
Best For: Large-scale manufacturers and service centers prioritizing quality and scalability.
How to Select the Right Leveling System: A 4-Step Framework
1.Assess Material Specifications
2.Evaluate Production Volume
3.Define Quality Standards
4.Analyze Budget and ROI

Emerging Trends in Sheet Metal Leveling Technology
1.Smart Levelers with IoT Integration
2.Eco-Friendly Innovations
3.AI-Driven Adjustments
Case Study: Precision Leveling in Automotive Manufacturing
A leading automotive supplier reduced assembly line defects by 40% after switching to precision levelers. By eliminating internal stresses in stamped components, they achieved:
Faster welding cycles.
Improved paint adhesion.
Lower warranty claims.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Fabrication Process with the Right Leveling Solution
From manual presses to AI-powered systems, sheet metal leveling technology continues to evolve. For SMEs, rolling machines or simple levelers offer a practical start, while large enterprises benefit from precision systems’ speed and accuracy. By aligning your choice with production needs and industry trends, you ensure higher-quality outputs, reduced waste, and a stronger market position.
Stay ahead in the metal fabrication industry by adopting advanced leveling techniques that prioritize both quality and efficiency.
MORE: sheet metal flattening techniques, precision roller levelers, reduce internal stress in metal, sheet metal straightening methods, advanced metal fabrication tools.




